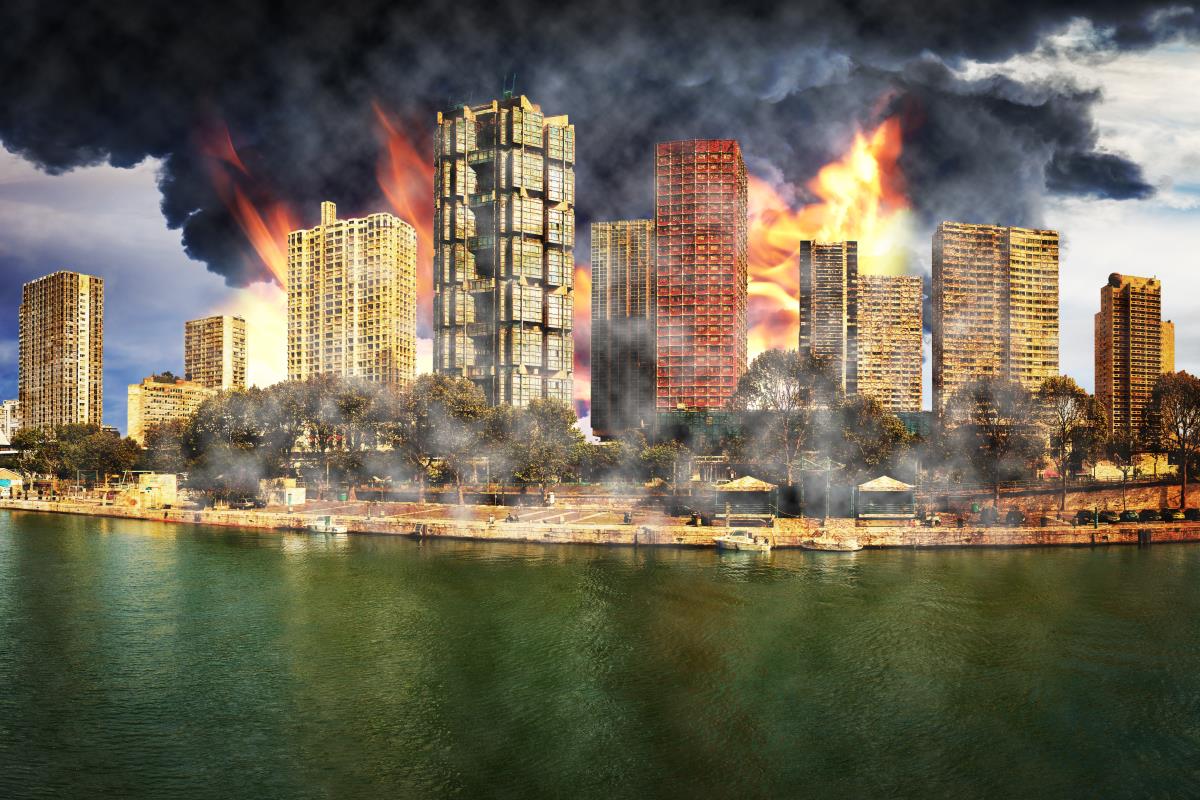
Massive earthquake is forming under New York City… and it could be unleashed without notice
09/07/2017 / By Michelle Simmons

New York may seem like the least earthquake-prone region in the U.S., but experts warn that a possible massive earthquake could happen in the area. Journalist Kathryn Miles made this claim in her book, Quakeland: On the Road to America’s Next Devastating Earthquake.
In a book excerpt posted on The Daily Beast, Miles wrote that most of the faults in New York fall into two groups: those running northeast and those running northwest. These faults, combined, create a “brittle grid” underlying Manhattan which could load up a massive quake.
Geologist Charles Merguerian has been studying these faults for the last 40 years to assess their seismicity. He then mapped all of them into an understandable map in 150 days, providing the first definitive proof of just how many faults really lie below the city’s surface.
Merguerian primarily looked for what geologists call “offsets.” These are places where the types of rock do not line up with one another. These irregularities show signs of movement over time, a clear evidence of a fault. And he has found thousands of them underneath New York City.
While there have been small quakes in New York, including a magnitude 2.6 that struck in October 2001, records show that the last time a major quake with a magnitude 5.0 shook the city happened in August 1884 and a relatively massive one in 1737. As we look at these records, the large quakes happened every century or about 150 years. Merguerian says that the city is overdue for another one; however, there is no exact date of when this destructive shake will happen. (Related: Earthquake scientists have been totally WRONG: Quake risk “dramatically underestimated” warns new report.)
Sponsored solution from the Health Ranger Store: Lab-verified Nascent Iodine solution is a dietary supplement that provides your body with supplemental iodine to help protect your thyroid during radiation exposure. Nuclear accidents such as Fukushima (or nuclear war) can expose your body to radioactive iodine-131, a dangerous radioisotope. Pre-loading your system with stable iodine occupies the iodine receptor sites on your organs, causing your body to naturally expel radioactive iodine you may have been exposed to through air, food, water or milk products. This defensive strategy is recommended by nearly all health authorities, worldwide, including the Nuclear Regulatory Commission. Discover more at this link.
“An earthquake could happen any day, or it couldn’t happen for 100 years, and you just don’t know, there’s no way to predict,” Merguerian told the Daily Mail.
In response to the question of how overdue the Big Apple is, Merguerian advises us to “take the pulse of what’s gone on in recorded history.”
There is no way to predict when it may happen, unless we would have about ten times as much data as we do today. However, his records show that the faults underneath New York are very much alive.
According to a report by the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), 42 out of the 50 states have a reasonable chance of experiencing a damaging earthquake in the next 50 years.
The USGS report also explained that the east coast has the potential for larger and more damaging earthquakes than previously thought. The report explained that the maps in New York City indicate a “slightly lower hazard for tall buildings than previously thought (but still a hazard nonetheless).” Scientists also estimated a lower likelihood for slow shaking from an earthquake near the city.
“Slow shaking is likely to cause more damage to tall structures in contrast, compared to fast shaking which is more likely to impact shorter structures,” the USGS report continued.
Until today, there is not enough information gathered regarding the seismic activity in the region, and this alarms experts.
“We just have no consciousness towards earthquakes in the eastern United States,” says Merguerian. “And that’s a big mistake.”
Read more stories like this on Disaster.news
Sources include:
Tagged Under: disaster, earthquake, earthquake risk, natural disaster, New York, NYC